
In other words, peas are diploid organisms in that they have two copies of each chromosome. Each pair of homologous chromosomes has the same linear order of genes. The genetic makeup of peas consists of two similar, or homologous, copies of each chromosome, one from each parent. Physical characteristics are expressed through genes carried on chromosomes.
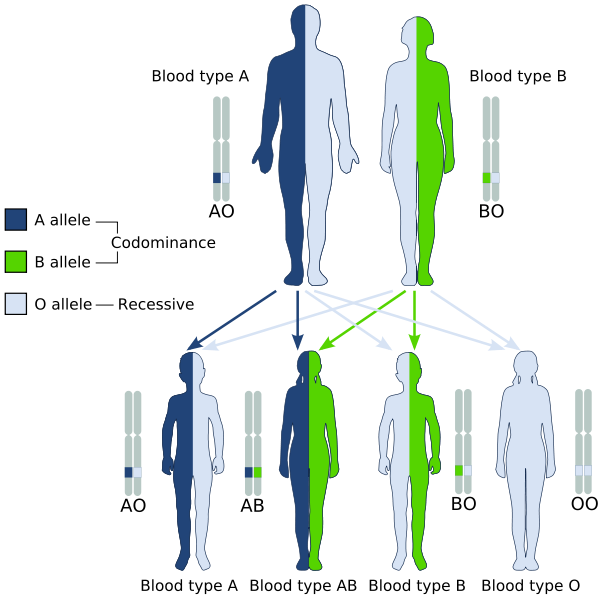
Identify non-Mendelian inheritance patterns such as incomplete dominance, codominance, recessive lethals, multiple alleles, and sex linkage. Explain the purpose and methods of a test cross. Develop a Punnett square to calculate the expected proportions of genotypes and phenotypes in a monohybrid cross. Explain the relationship between genotypes and phenotypes in dominant and recessive gene systems. For example, short cat hair could result from either of two genotypes, LL or Ll.By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following: Phenotype is also influenced by environmental factors, and a single phenotype could be the result of more than one genotype. Genotypes influence phenotypes, but they are not always perfectly correlated. The genotype corresponding to the phenotype of short coat length would be either LL or Ll, while the genotype for long coat length would be ll. In cats, one phenotype example is coat length. In humans, phenotype examples are eye color and hair color. In other words, the genotype refers to the genetic information, while the phenotype refers to the observable characteristics, including traits. Phenotype is the term for all the observable characteristics for which the genes code. Genotype refers to all the genes that an individual carries. The allelic combinations between the rows and columns represent the probable genotypes of the offspring. If the diagram represents one gene with two alleles, there are two rows and two columns, one for each allele. This is essentially a grid that contains one parent’s genotype as a column and the other parent’s genotype as a row. In order to obtain this probability, a diagram known as a Punnett square can be used. The likelihood of offspring having a particular genotype is known as the genotype ratio. There are two homozygous genotypes for cat coat length: LL (homozygous dominant) and ll (homozygous recessive). The heterozygous genotype for cat coat length is Ll, with one allele (L) coding for a short coat and one allele (l) coding for a long coat. Homozygous genotypes have two copies of the same allele. Heterozygous genotypes contain one copy of one allele and one copy of the other. Genotypes can be described as heterozygous or homozygous. This can be seen in snapdragons, where a red allele and a white allele give a pink flower. Other times alleles might be incompletely dominant. In this case, if someone has an A allele and a B allele, they have AB blood type. Sometimes, as in blood type, two alleles might be codominant-they combine to make a trait. Not every allele is dominant or recessive. So in the case of cat fur length, “L” refers to the short hair allele and “l” to the long hair allele. Geneticists denote dominant alleles with a capital letter and recessive alleles with a lowercase letter. 
If it takes just one allele to see a trait in a diploid organism, then that trait is dominant. In this case, the short allele is said to be dominant over the recessive long allele. And if it has one of each, it has short hair. If it has two long alleles, it has long fur. If a cat has two short alleles, it has short fur. For example, in cats, fur length is decided by a gene that comes in two versions, short and long. Genotype and AllelesĪlleles can combine in different ways to affect some aspect of a living thing. In humans, the gene for earwax type, for example, has two alleles: one for wet earwax and one for dry earwax. The exception to this is in biological males who have a single X and a single Y chromosome.Īt a given position in the DNA (or genetic locus), the pair of alleles from the two chromosomes makes up the genotype at that position. Humans are diploid organisms, which means you have two copies of each chromosome-one from each parent. For example, if your MC1R gene leads to you having red hair, then you have the genotype for red hair. Genotype can also refer to a gene or set of genes that leads to a single trait or disease. In humans, it’s why one person might have red hair and another person might have blonde, or even why someone is less likely to end up with type 2 diabetes or have a heart attack. It is why some peas are wrinkled and some are smooth. It is the set of instructions that controls most everything about an organism. A genotype is the collection of genes that all living things, including you and everyone you know, carry.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
